

by Editor
The buzz around deepfake technology has been going on for years, although it was only last year that their creation and use reached a new technical level due to serious improvements in AI algorithms. We delve into the topic of deepfakes and explain how to create them for free, following a simple guide.
What is a deepfake?
Deepfake is a technology that allows "bringing to life" and visualizing photorealistic images of people using artificial intelligence algorithms. To create a video with a deepfake, neural network algorithms analyze a large number of images, identifying characteristics of behavior, facial expressions, gestures of the main character, and so on.
The term "deepfake" is constructed by combining two concepts: "deep learning" and "fake".
Deepfakes aren’t only used in creating videos. With the help of voice deepfakes, scammers and crooks attempt to deceive people to extort money.
In arbitrage, deepfakes can be used to create creatives with characters posing as celebrities to promote products, services, or offers.
When did the first deepfakes appear?
The first prototypes of deepfake technology emerged as early as 1997. The Video Rewrite program allowed for the manipulation of facial expressions and the substitution of any voice audio tracks.
Example of the Video Rewrite program in action:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5ymelRjHIfI
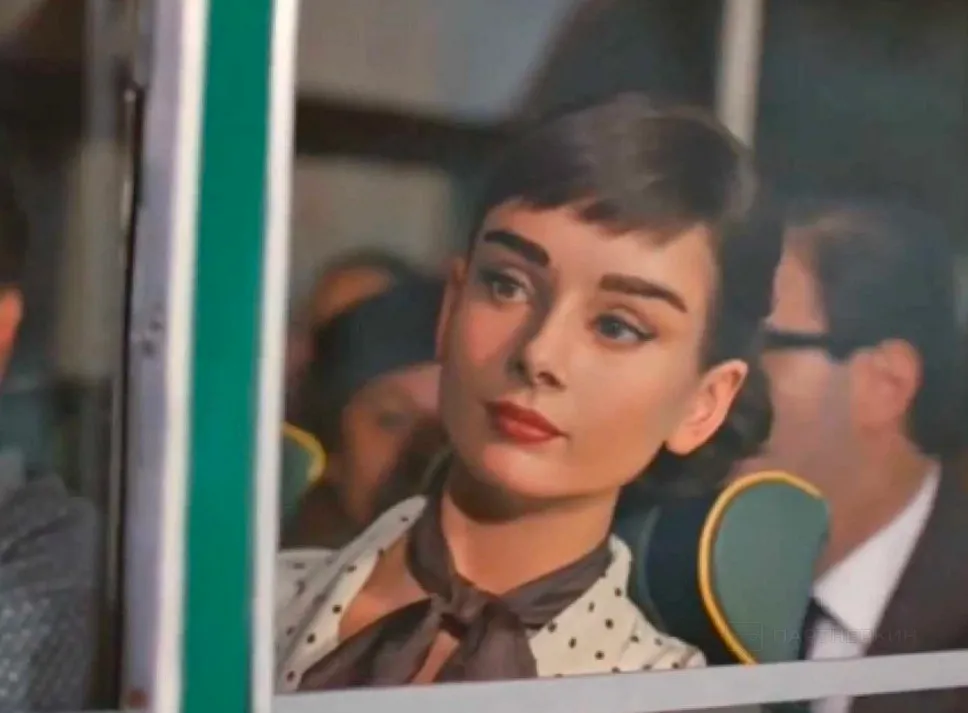
In 2014, the famous Dove chocolate advertisement featuring a lifelike image of the renowned British model and actress Audrey Hepburn emerged. In the commercial, the computer-generated "actress" travels through Italy, meets a charming young man, and drives off into the sunset with him in a convertible. The overall atmosphere of the video is stylized to resemble the 1950s, with references to famous films starring Hepburn such as "Roman Holiday", "Funny Face", and others.

At the same time, GAN emerged as one of the first AI models used to create complex deepfakes. GAN stands for Generative Adversarial Network. Technically, the model operates with a generator, which produces realistic images, and a discriminator, which distinguishes between fake and authentic materials, acting as an internal "expert" in selecting the final creative.
Initially, in GAN, it wasn't possible to input custom prompts for generating images. The AI would autonomously generate random images based on the examples stored in its memory. As a result, the algorithms could only visualize small, low-quality images of faces.
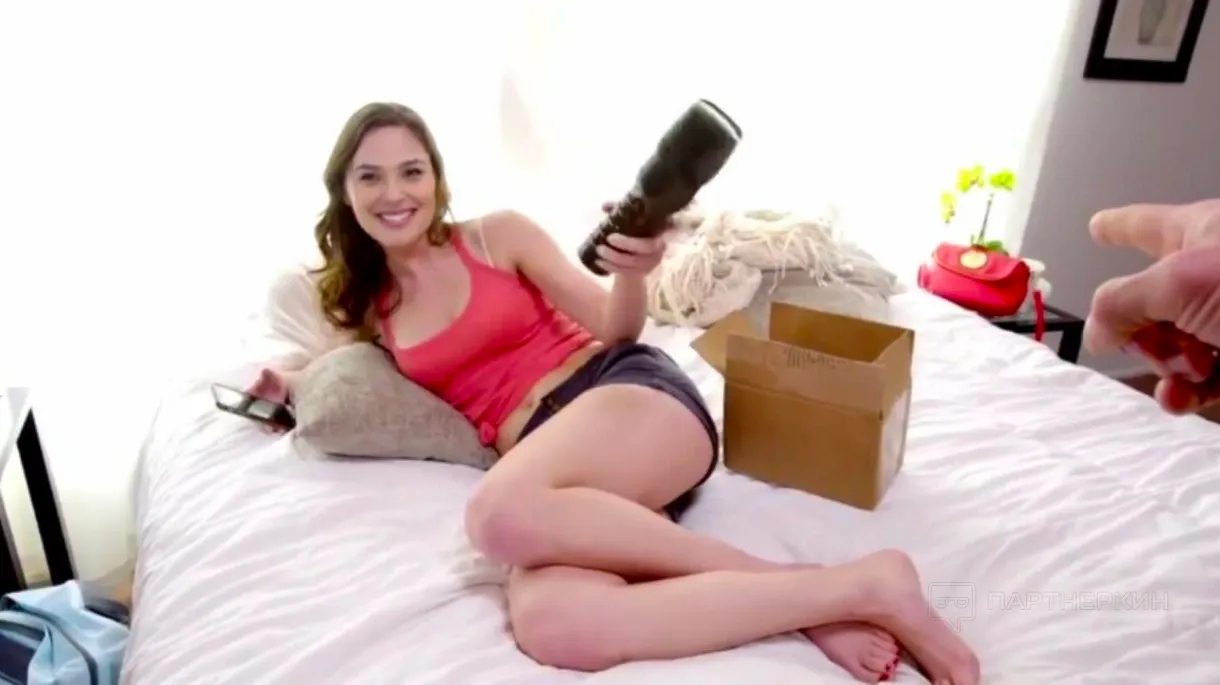
The first decent-quality deepfakes generated with the help of AI appeared in 2017. The most notable case of using this improved technology was associated with a user named Deepfakes, who posted several intimate videos on Reddit featuring fake nude celebrities. Scarlett Johansson, Emma Watson, Maisie Williams, and Gal Gadot were among the victims portrayed in those videos.
Fake Gal Gadot in one of the Deepfakes videos:

When creating porn, Deepfakes used machine learning algorithms from TensorFlow, which Google provided for free to scientists, researchers, and anyone interested in cutting-edge technologies. Even then, experts noted typical shortcomings of such deepfakes: while the human figures appeared realistic, close examination revealed incorrect fine details and movements.
After the resonant case with Deepfakes, serious people with money became interested in the new technology. Like mushrooms after rain, dozens of software companies began to appear, offering their solutions for generating videos, audio, and even full-fledged narrative scenes.
The number of subscribers on YouTube channels that posted deepfake videos with famous personalities, such as Shamook and Ctrl Shift Face, noticeably increased. The first fully virtual characters created with AI and living on Instagram* also appeared — girls like Lil Miquela, Shudu Gram, and Imma. At the same time, the first services emerged that allowed ordinary people to create simple deepfakes, for example, the ReFace app.
Jim Carrey "playing" Jack Torrance in one of the most famous scenes from Stanley Kubrick's 1980 film "The Shining": https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HG_NZpkttXE
Where deepfakes are used
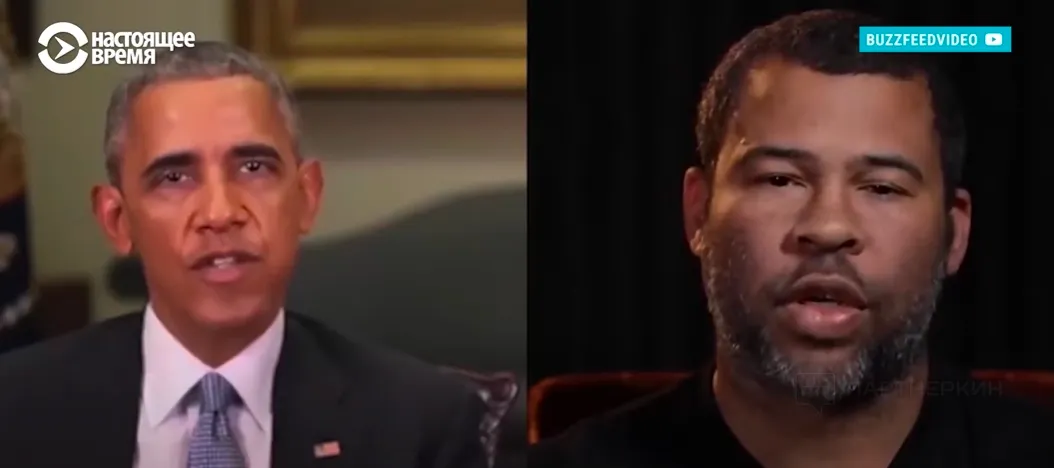
Among the sensational cases associated with deepfakes, purely political ones immediately appeared. Drunk Nancy Pelosi, Donald Trump speaking out against environmental initiatives, and Barack Obama allegedly calling Trump a "total and complete dipshit" are just a small part of the noise generated by neural networks even before the AI boom.

In 2023, on the wave of a revolutionary leap in the development of artificial intelligence as a whole, the internet was flooded with deepfakes created at a new quality level. In May 2023, Reuters, citing the AI company DeepMedia, reported that compared to 2022, the number of video deepfakes had tripled, and audio deepfakes had increased eightfold.
Deepfakes are used in all sectors of human activity where images, videos, or sound play a significant role. They are applied not only for good but also for harm — criminals were among the first to try using the new technology in their trade.
According to the AI Index Report 2023, the number of ethical violations related to the use of deepfakes has increased by 26 times over the past 10 years. At the same time, research by Onfido shows that the number of fraud cases related to the technology increased by 30 times in 2023 compared to the year before last. Interestingly, in 80.3% of cases, fraudsters used relatively simple schemes — 7.4% more often than in the year before last.
Negative consequences of deepfakes include their use in the pornography industry. A study conducted by Deeptrace in 2019 showed that 96% of all fake materials online are related to "adult content". In 2023, the volume of deepfake pornography increased by 464%. In particular, experts at Home Security Heroes determined that over 280 000 pornographic videos created using AI technologies have been uploaded online. The scale and popularity of such content is evidenced by the number of views, which exceeded 4.2 billion.
The risks of AI-generated deepfake pornography are associated with cyberbullying, blackmail, and extortion. Neither adults nor teenagers are immune from this: one of the recent high-profile scandals involved a 14-year-old student from Westfield High School in New Jersey.
Despite the negative implications associated with the use of AI-generated deepfakes, it cannot be said that they are entirely evil. This is because deepfakes also bring benefits to people.
First and foremost, they often contribute to the spread of transformative societal content. One prominent example is the story of the school shooting victim Joaquin Oliver. With his parents' consent, activists integrated his image into an emotionally charged social video advocating for gun control in the United States.
Video featuring Joaquin Oliver: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m6I_wEetSck
Deepfakes are also used beneficially in the arts. For example, at the Dali Museum in Florida, USA, an AI-generated image of the world-renowned artist greets visitors at the entrance, narrating about art and the creativity of the brilliant Spaniard. In this project, the speech for the neural-painter was "written" by artificial intelligence based on numerous interviews. The voice actor for the deepfake reproduces Dali's unique accent, blending English, French, and Spanish. Creating the digital copy of the artist required 6000 photos, 1000 hours of machine learning, and 145 videos with an actor of similar proportions.
The AI algorithms in the synthesized audio voice of the Seeing AI app help blind and visually impaired people navigate their surroundings.
Engineer-researchers Wei Zheng and Kate Glazko use deepfakes to assist people with aphantasia, those who lack imagination and are unable to create abstract images. Using a special program, scientists reproduce various life circumstances that help rehearse behavior in stressful situations in advance and reduce anxiety levels.
Deepfakes also help people learn, acquire new skills, and professions — there are many services now that can be customized for any educational or seminar task. An international study by Wyzowl concludes that 68% of enterprise employees prefer educational videos to articles, infographics, presentations, and books. AI tools for creating deepfakes allow for quickly and cost-effectively producing any instructional video in any business or industrial sector.
How to make a free deepfake in a video
Typically, moneymakers need to use AI to replace the face of a character with another for promoting an offer or product. Replacing faces is popular in creating dating creatives with elements of prohibited content.
In the network, you can find many services that offer creating deepfakes. The downside is that free versions are usually heavily limited in functionality, and not everyone is willing to pay even a small amount to generate 1-2 videos.
However, making a free deepfake yourself isn't that difficult — just follow the instructions below.
To replace a face in a video, you won't need to spend a long time training the generative model by trying hundreds of photos with different expressions. You just need one photo of decent quality and access to a computer with an Nvidia GPU. Making a deepfake on a PC with a CPU is significantly slower.
You'll also need access to Google Colab, a free service that allows you to run and use various scripts/applications on Google's servers.
Free usage of Google Colab is available for 6-12 hours, after which you'll need to take a 24-hour break, or you can purchase a subscription right away.
Instructions for creating a free deepfake video:
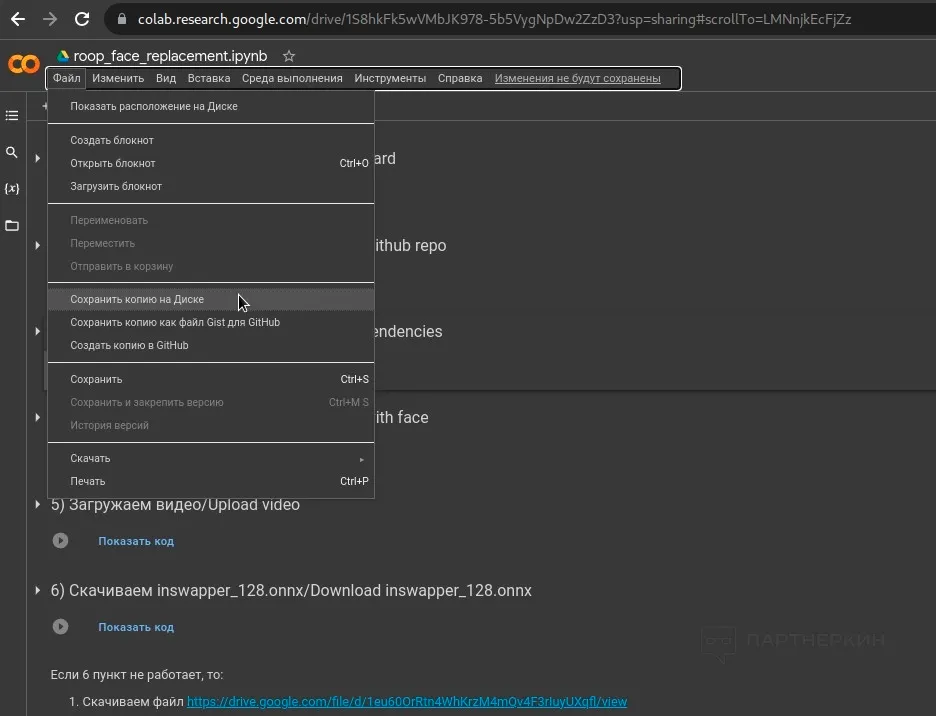
1. After logging into the Google system, navigate to the page with the configured neural network script and use the command "File > Save a copy to Drive" to transfer all files to your cloud storage. Upon successful transfer, the neural network will open on the tab of your personal web address.
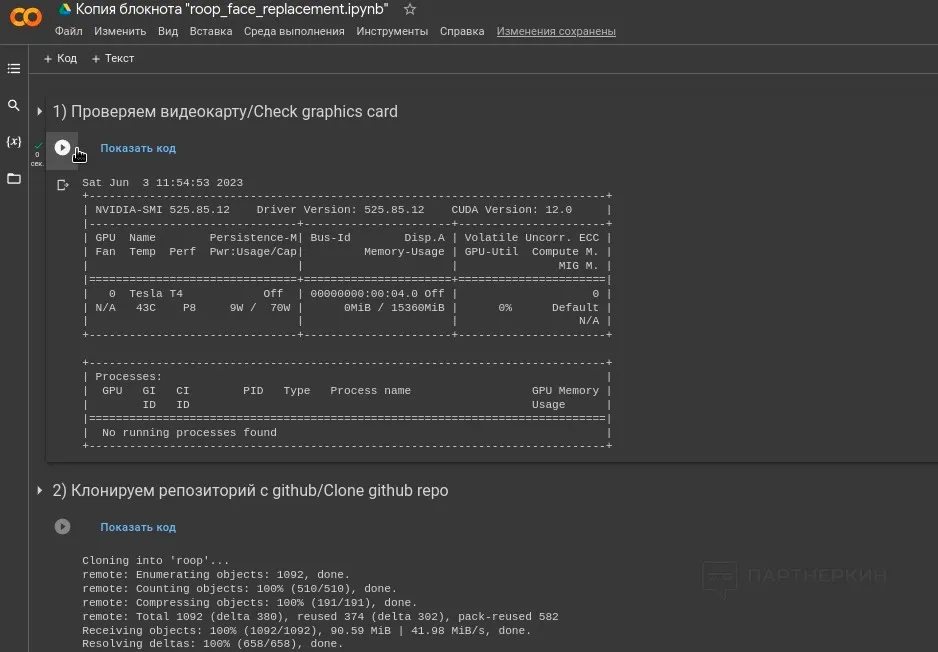
2. Run the GPU availability check script — the algorithm needs to ensure the presence of a graphics card, as calculations for future video on the CPU could take too much time. A schematic table with data will appear upon successful verification. If the table doesn’t appear, you can try running the process in Google Colab using another Google account.
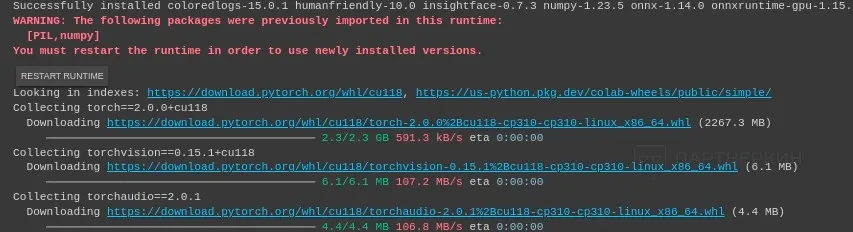
3. After that, you'll need to clone the repository — the web archive — of the neural network using script number 2. Upon its launch, immediately activate the installation of the main dependencies by clicking on button number 3.
During the installation of the setup scripts, the system may throw errors, but there's no need to worry about them — they don't affect the AI algorithm's operation. Pay attention only to the window with an error that contains "Restart Runtime" — in this case, you'll need to restart the installation of script 3.
4. On the next step, you need to run the script to upload a photo with the face that will be used in the video. Also, run script number 5 and select the final video for the deepfake.
When choosing the video, keep in mind that there should be only one actor in the frame. Videos with multiple people are acceptable if the faces of non-primary characters are somehow hidden.
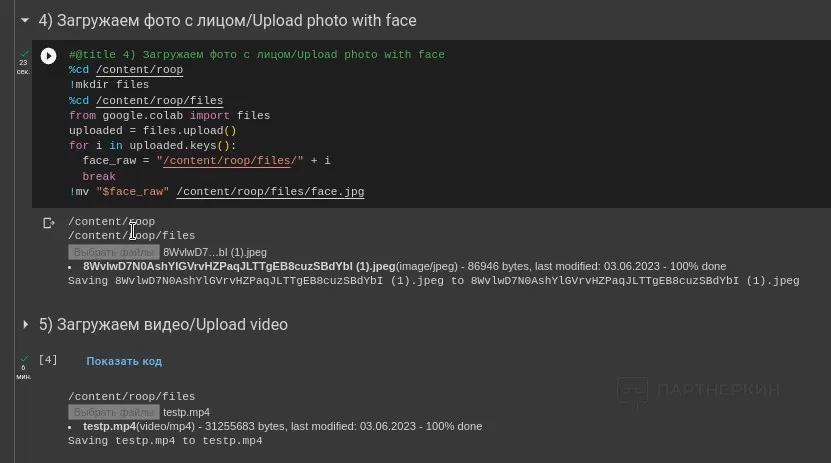
5. On the last step, check the box and run the script for the face replacement process. Then, wait for the file processing to finish: rendering a five-minute video may take 30-40 minutes.
6. After the message "Status: swap successful" appears, the finished video can be downloaded. To do this, find the option "face_changed_video.mp4" in the left column and right-click to download the file.
How to make a free deepfake in a photo without Photoshop
To create a photo deepfake, you can use the same service Google Colab. Follow these instructions:
1. Go to the page of the configured script and copy it to your cloud. Upon successful action, the system redirects you to the personal web page of the script, which you need to save in your browser bookmarks.
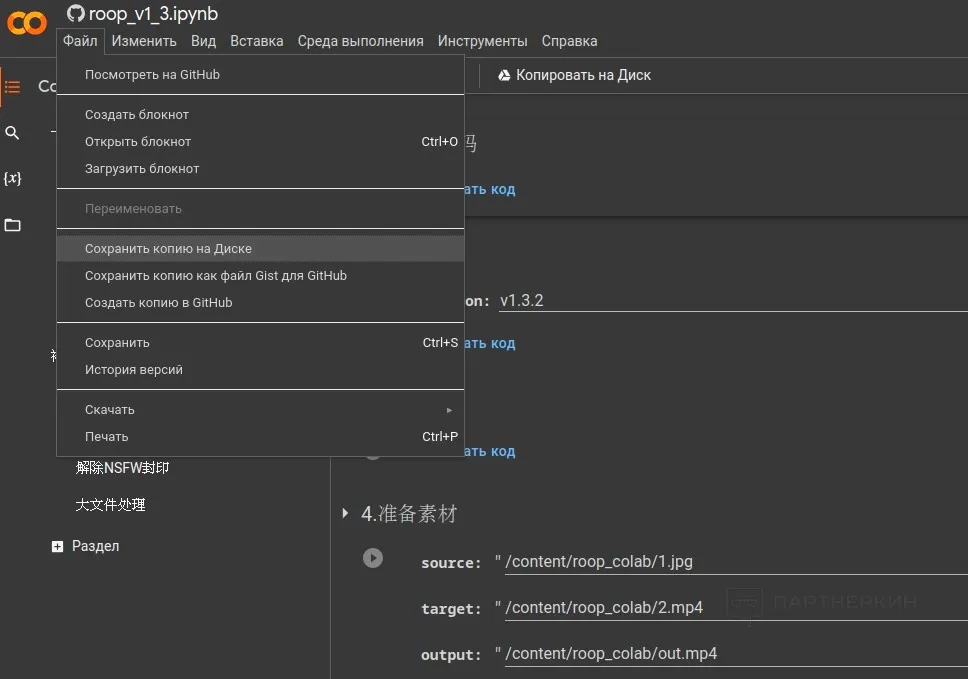
2. For convenience, you can translate hieroglyphs into Russian in Chrome by right-clicking and selecting the corresponding command.
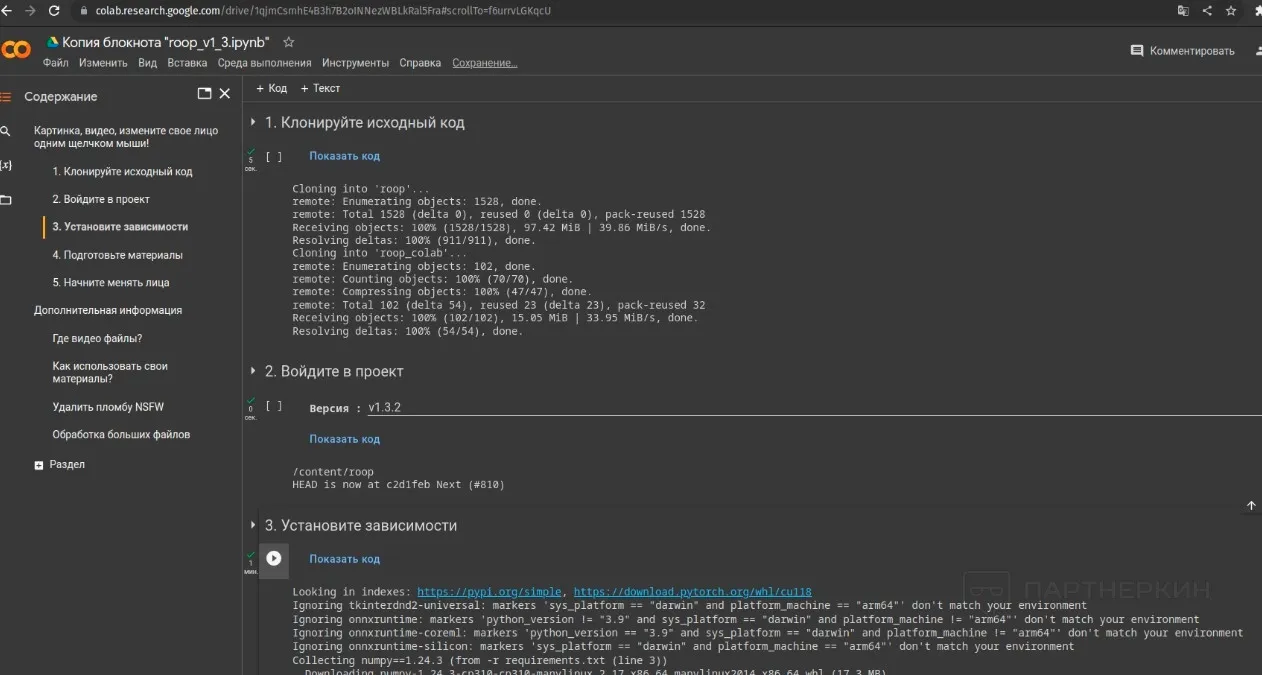
Then, run the first three items of the script in order. The process is complete when a green symbol appears next to the number — no GPU is needed for the algorithm to work. When executing the third script, errors may appear, but they can be ignored as they don’t affect the creation of the deepfake.
3. On the next step, we upload the photos for replacing the face into the neural network. In the left column, click on the button with the file tree icon, then right-click to upload the necessary photos for replacement into the "roop_colab" folder.
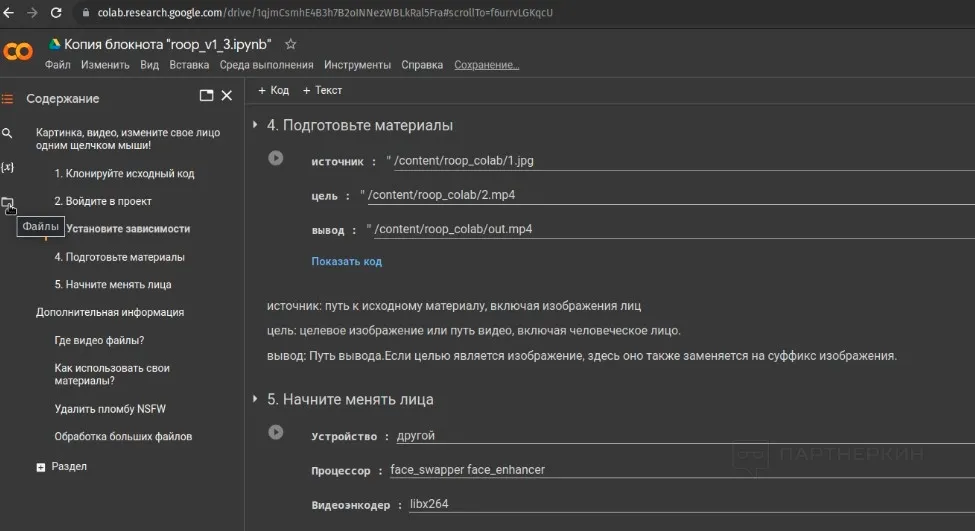
4. Next, in the 4th section of the script, we change the lines to the names of our uploaded files. In the "source" line, specify the photo with the face that needs to be inserted into the photo, and in the "target" line, specify the photo where this face will be inserted. Then, run the script.
5. In the last section of the script, you need to select the desired algorithm settings: you can set the same parameters as shown in the screenshot below.
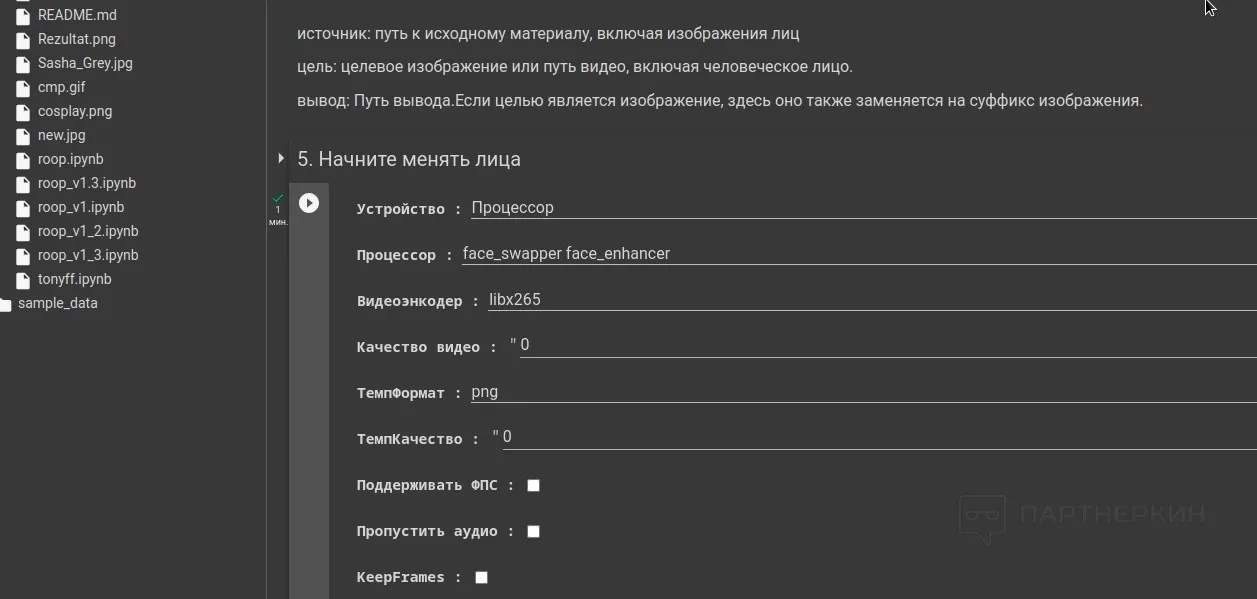
6. The process of creating a deepfake usually takes several minutes. If successful, at the end of the script console output, you’ll see the message [ROOP.CORE] Processing to image succeed. Also, in the left column, a file named "Rezultat.png" will appear. You need to download it by right-clicking.
How to remove censorship when creating a photo deepfake
When working with this AI script, the algorithm by default blurs images with spicy details. This problem can be bypassed by downloading the file predictor.py and using any text editor to change the parameter MAX_PROBABILITY=0.85 to MAX_PROBABILITY=1. After that, you need to upload the file back.
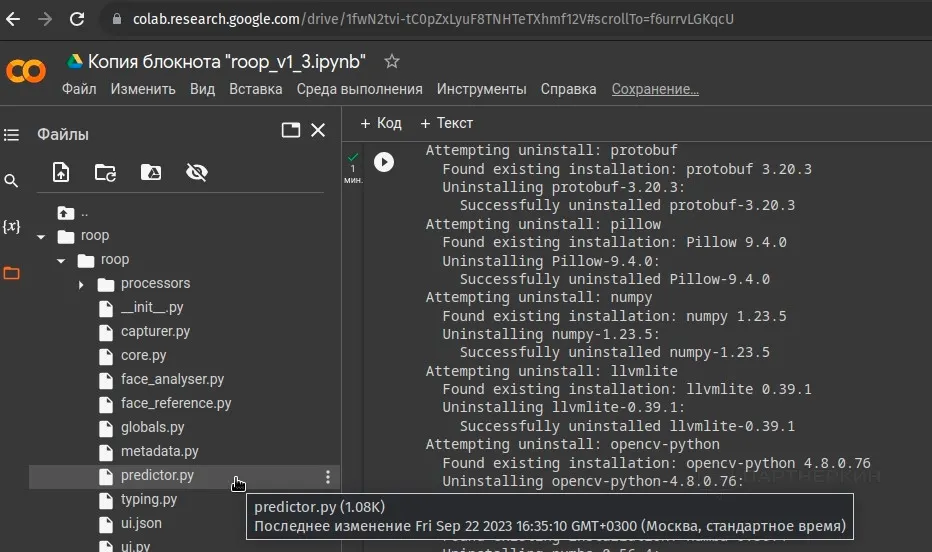
You can use the ready-made predictor.py file from this link.
Conclusions
Deepfakes have become a part of our virtual life for the long term, and the technology is likely to continue developing and improving. Creating a creative with a deepfake is easily achievable even for someone unfamiliar with programming. You can use any paid AI service or create one absolutely for free using the instructions from this article.

by Editor



comments ....(0)
Leave a comment
You must be in to leave a comment