

by Editor
In 2021, the use of traffic from residential proxy servers increased by 70%, while that from data centers increased by 60%. The annual revenue of market leaders exceeded $100 million. Companies are expanding their staff by 30% per year to connect more proxies and develop new products, such as proprietary software for parsing. However, this also means that competition is increasing. Yet, the technical entry threshold remains low. Let's try to understand how you can earn money in the proxy market nowadays.
Proxy market trends
Proxy providers are horizontally expanding, venturing into new niches and tools. The main focus is on releasing API interfaces for web scraping. This will allow services to create an ecosystem of their own products that will solve complex user tasks: from providing access and security on the network to parsing and analyzing data.
Residential and datacenter proxies remain the most in-demand among users, occupying 95% of the market. However, ISP proxies, which combine static and residential connection types, are gaining traction — they’re hosted on data center servers but their IPs are identified as real user addresses. Despite the hype, mobile proxies are still used for a narrow range of tasks, at least among clients of major providers.
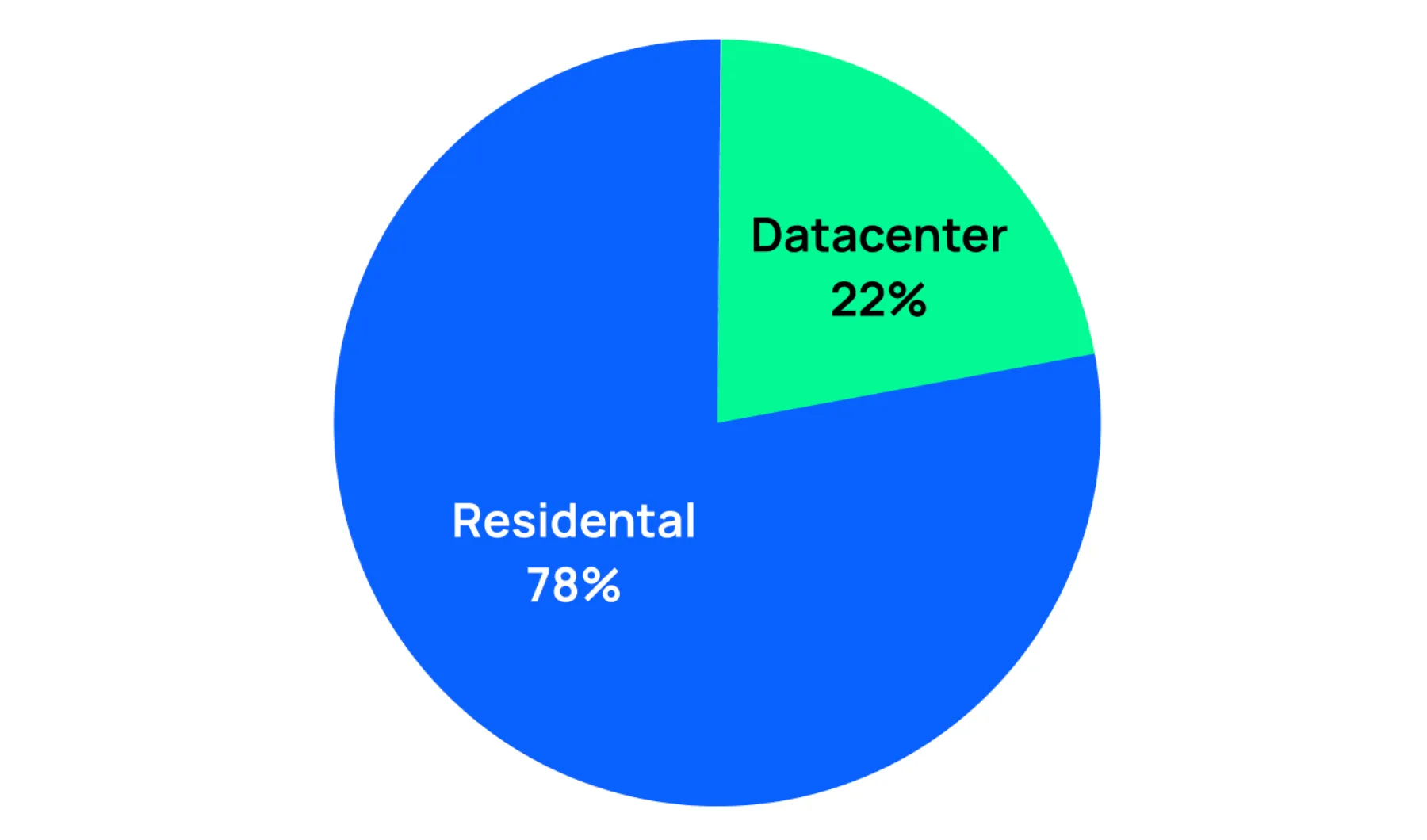
Let's take a detailed look at the main types of proxies, examine their development dynamics in the market, and compare them based on key parameters: effectiveness, speed, and price.
Datacenter (corporate) proxies
These are protocols running on servers in large data centers, such as Amazon Web Services and Google Cloud Platform. They are often used by corporations to secure internal networks. Such proxies typically have high bandwidth and speed. However, their IP addresses don’t belong to real users, making them easily detectable by websites tracking traffic. Popular parsing platforms, like Amazon or eBay, often know the IP addresses of data centers and proactively blacklist them.
Most datacenter proxy servers charge only for IP addresses, without limiting traffic or connection requests. Datacenter proxies operate quickly — their response time is several times faster than residential or mobile proxies — but they are the cheapest because of the low trustworthiness of IP addresses.
Residential proxies
These proxy servers use IP addresses of real people provided by internet service providers. The main advantage of residential proxies is their high level of anonymity and rare address blocking due to live, trusted IPs. Additionally, such proxies allow you to choose specific location: region, country, and city, and to target ASN providers to avoid attention from regulators and bypass geographical restrictions on the network.
Residential proxies form vast networks covering millions of IP addresses. The number of IPs in a proxy provider's pool characterizes the service level — 100 million addresses in the premium segment or several thousand in low-cost providers. Differences also arise in the availability of additional features. For example, targeting ASN remains a rare premium option. Based on these distinctions, the price of proxies is formed, usually depending on the amount of traffic in the subscription; payment based solely on the GB used is rare.
Mobile proxies
P2P proxies are servers located on smartphones or tablets connected to mobile networks. Mobile proxy pools are often smaller and significantly more expensive than residential or corporate proxies, but they have the highest level of anonymity on the network. This is due to the peculiarities of mobile internet operation.
Mobile operators technically cannot assign a static IP address to every subscriber connected to the internet. They distribute their own limited pool of IPv4 addresses among millions of users using NAT algorithms. Therefore, thousands of subscribers can be using the same mobile IP address simultaneously. As a result, blocking any suspicious address will lead to banning numerous users, and losing the target audience is highly undesirable for major internet resources.
Mobile proxies based on USB modems with SIM cards inside, using a special script, transform into a separate server. Compared to peer-to-peer networks, this setup allows for better control over individual IP addresses and increases the uptime of proxies with on-demand rotation. Recently, this type of service has become popular among users. For instance, about 20 new mobile proxy providers have emerged on the popular BlackHatWorld forum in the past year, confirming that the demand for mobile proxies is growing and there are still vacant niches for new players in the market.

Proxy based API
These tools typically consist of a combination of datacenter and residential proxies. Their purpose is to simplify the work of users who need to gather large datasets. API interfaces allow for the successful handling of complex web scraping tasks through dynamic IP rotation, built-in CAPTCHA bypass, and browser fingerprint hiding. Moreover, they save clients time by delivering ready datasets upon request in the shortest possible time frame. This method of data acquisition is becoming increasingly popular and is used for parsing complex networks, such as Google or Amazon.
Where do proxies come from
Every device connected to the internet has its own IP address — a unique combination of numbers that can be used to trace the source of actions on the network. For example, based on an IP, it's easy to determine the country, city, and internet service provider of the device. An address can be banned due to suspicious activity or access to a resource may be restricted for residents of certain countries.
A proxy server is an intermediary between a user and a website. It redirects connections through different IP addresses, allowing the user's real address to be masked. Proxies are used to bypass bans and restrictions on the internet, as well as to enhance privacy and security while browsing. Creating proxy servers requires many machines with clean IP addresses. These can be user devices, individual modems, or entire farms.
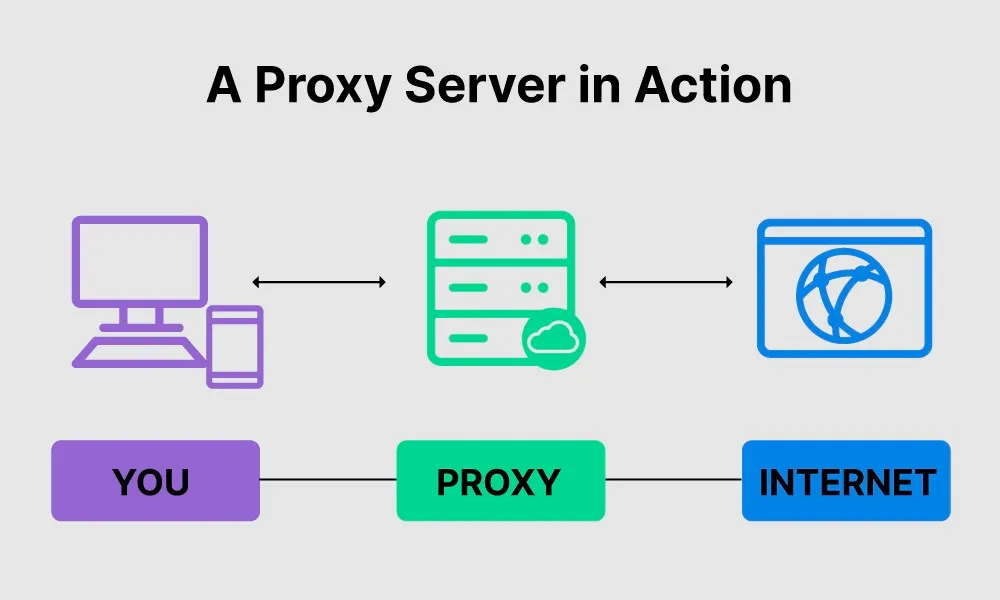
Modem farms are the most expensive way to obtain proxies. A small farm of mobile proxies with 10 ports will require investment in infrastructure and a lot of time for assembly and configuration. 10 modems, their firmware, a 10-port USB hub, 10 SIM cards, and a paid server will cost around $1000 altogether. However, similar proxies can be purchased from a provider for approximately $50 for 3 months.
Data centers — their own hardware on live servers generates high production capacities that can be used to create proxies. Datacenter proxies will have high speed, but they are easy to track — such proxies use IP addresses of large ranges, so services ban them with entire subnets. Datacenter proxy traffic is the cheapest, but to build and maintain the infrastructure, you’ll need to spend the budget of a small city.
Earn apps are those applications for earning money by viewing advertisements. They are openly promoted and distributed in app stores. Earn apps often directly offer to become a participant in a peer-to-peer proxy network for a small reward. They are mainly used to mine mobile proxies, and less frequently, residential proxies when installed on a computer. Examples of such applications include AdWallet, AdMe, and CashNGifts. Recently, Google Play has been cracking down on Earn apps and removing them from the store, even if the apps honestly warn users that they’ll become part of a proxy network.
SDK (Software Development Kit) is a library of ready-made solutions for developers, containing APIs, code snippets, documentation, and other tools. They are often hidden inside applications and can turn a device into a proxy server without the user's knowledge upon installation. SDKs are mainly promoted through free VPNs or other utilities and rarely warn users that their devices become part of a proxy network. Even current market leaders like Bright Data, formerly known as Luminati in 2013, were caught up in SDK manipulations through an application, leading to a PR scandal and rebranding.
A botnet is the “darkest” method of proxy farming. It’s a network of infected devices transmitting data to the main host and executing its commands. Devices can be anything: PCs, tablets, smartphones, even a car with an onboard computer. Botnets particularly target corporate networks, where there are many devices, and if the defensive barrier is overcome, multiple devices can be hijacked at once.
A classic IoT botnet consists of tens of thousands of infected devices, which are controlled through a C&C server. During propagation, the malware scans for IP addresses of devices, identifies poorly protected ones, and compromises them. The virus enables remote execution of any actions using the computational resources of the infected machines.
As a rule, botnets are used for DDoS attacks, mining, and phishing. Additionally, devices can be turned into proxy servers and traffic can be sold to other users. This is the cheapest and most common way to obtain proxies for illegal activities on the internet. Every 2-3 years, the police conduct investigations and identify hackers who launched the virus, but new botnets quickly replace the closed ones.
Why are proxies needed
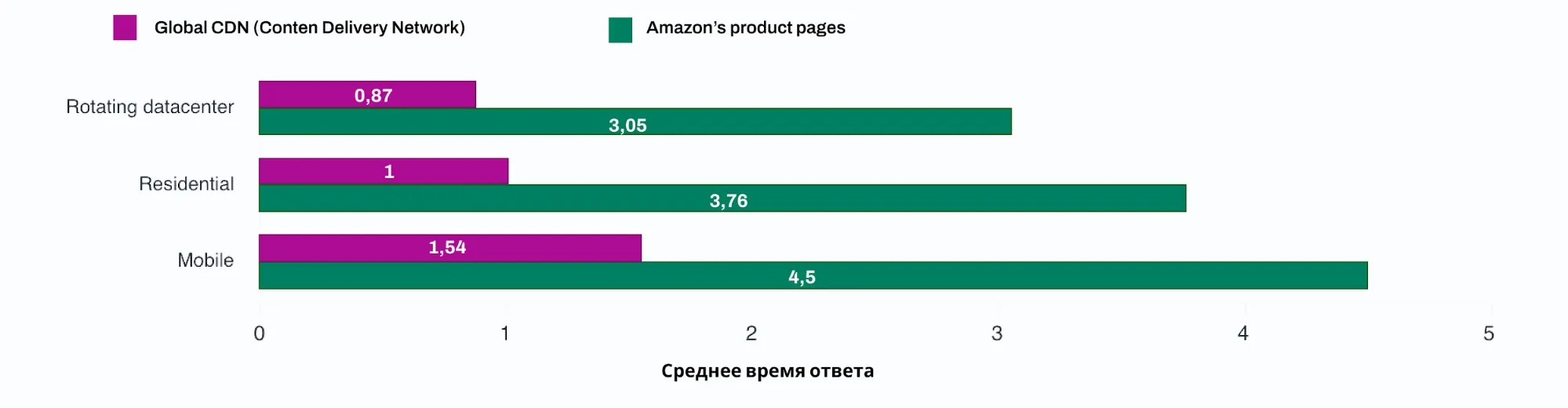
Knowing all the use cases for proxies is impossible. However, we can identify the main areas where proxies are useful for businesses. Clients often use proxy connections for data parsing, analyzing ad placements, and monitoring the effectiveness of marketing campaigns. More details on the proxy usage spheres can be found in the chart.
How proxies are sold
Compliance with laws, reputation management, aggressive marketing by competitors — are just part of the challenges a proxy provider faces when entering the market. Building a reliable infrastructure requires financial investment, and the constant struggle for customers necessitates finding thematic platforms, creating content for them, and purchasing advertising from influencers.
The main feature of proxy distribution is the use of darknet forums. The majority of the target audience is still there: users are actively communicating, interest-based communities are being created, and service providers' advertisements are being published. To establish a presence on a forum, a proxy provider needs to receive positive reviews from regular users and invest in banner advertising in relevant sections. For example, the cost of a single advertising post on BlackHatWorld starts from $500, and an average proxy provider makes about 100 placements on various platforms per month.
Another way to distribute proxies is to sell them to large providers. This approach doesn't require investment in marketing or constant infrastructure development. Mobile proxies generated from small farms, which provide trusted IP addresses, are often sold in this manner. Larger companies willingly acquire them to expand their market presence.
One of the new and interesting approaches is embedding private proxy traffic into a provider's shared pool. Excess traffic can occur spontaneously, but you can earn extra income from it. For instance, Proxysell purchases all types of proxies, calculating the cost per GB based on GEO and IP cleanliness. The service aggregates the acquired traffic and sells it in bulk to global providers, while users receive rewards to crypto wallets.
That's all for now. If you have any questions, feel free to write them in the comments. I'm not sure whether to write the second part of the review or not. But if the article becomes popular, I'll explain how to set up infrastructure for $100 and start earning by selling proxies.

by Editor



comments ....(0)
Leave a comment
You must be in to leave a comment