

by Editor
In this article, we’ll discuss how to properly organize work with accounts on various services such as Google, TikTok, Facebook, LinkedIn, Bing, using an antidetect browser. We’ll explore what a digital footprint is, what data websites collect about us automatically, and examine the main digital fingerprints. I’ll briefly explain how these fingerprints are formed and provide practical tips to increase trust in your accounts.
What is an antidetect browser, digital fingerprint
An antidetect browser is specialized software designed to mask or alter a user's digital fingerprint on the Internet. A digital fingerprint (or browser fingerprint) is a unique combination of data that your browser automatically sends to websites when visiting them (for example, information about the browser type, operating system, screen resolution, installed plugins, and other settings). This data can be used to identify and track users online, which is often used for advertising, analytics, or censorship purposes.
The main functionality of such browsers is significantly extended. You can share data with team members, hide information about the mechanical side of the computer, and automate some processes.
Let's break down the concept of "Digital fingerprint". This term can be interpreted in two ways:
Active digital fingerprint refers to information that users consciously leave on the internet through their actions and interactions. Unlike passive digital fingerprints, which are collected without the explicit knowledge of the user, an active digital fingerprint is created when users themselves choose to share information online. This can include email addresses, phone numbers, addresses, comments, and messenger accounts. We won't delve into this type in detail in this article; we are more interested in the other aspect of the digital fingerprint.
Passive digital fingerprint refers to the collection of data about a user without their active participation. Typically, this includes information automatically gathered by systems and devices when using the internet, mobile applications, various services, and devices. Passive digital fingerprints may encompass search history, details of visited websites, location data, information gathered through cookies, and unique identifiers of your PC (Fingerprints).
A fingerprint is the unique digital signature of your browser, and its masking is the primary goal of Antidetect browsers.
Let's see what information websites collect about us using the example of the Browserscan website.
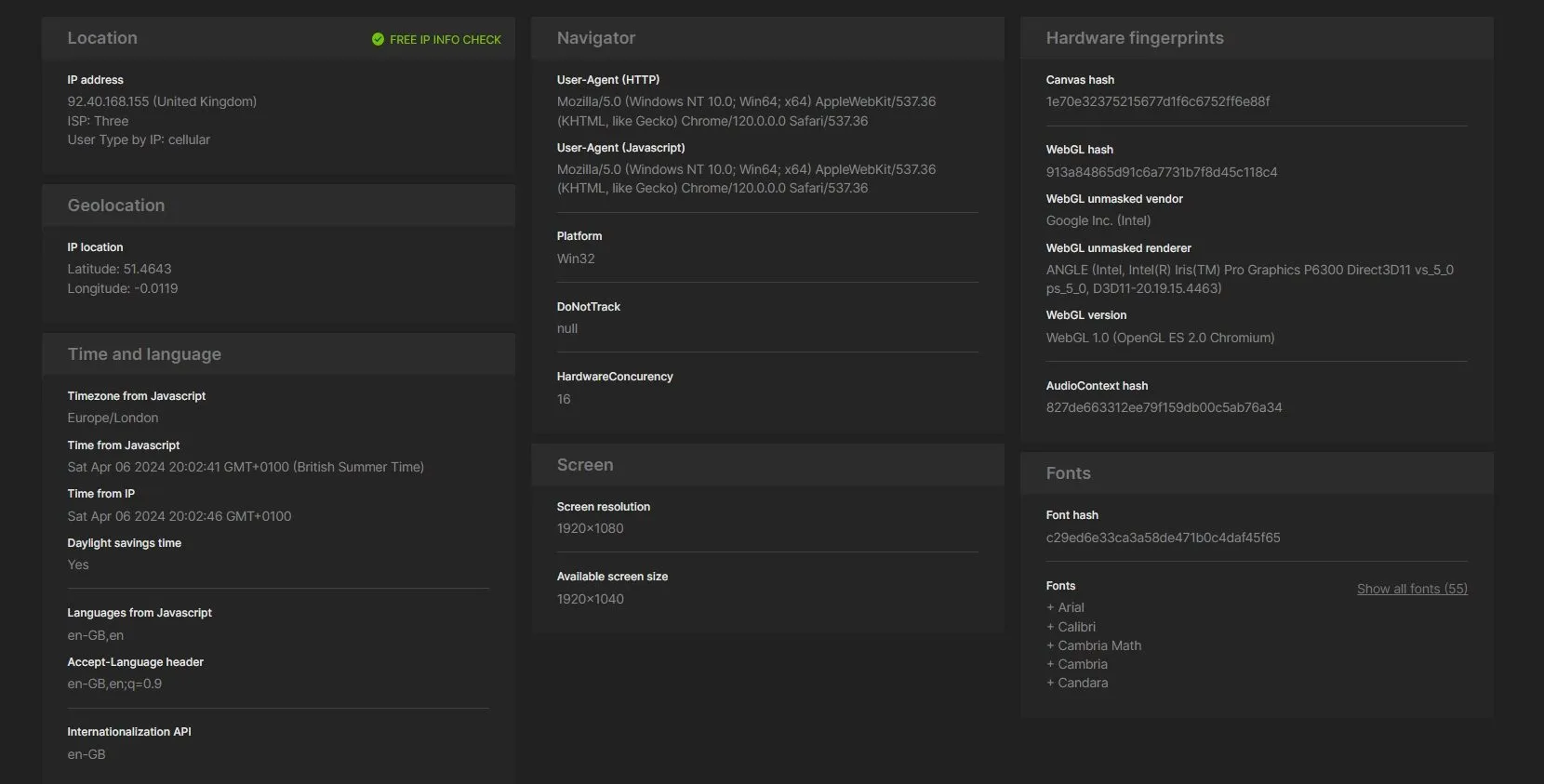
Any website can see all this information about you, and it doesn't need any permissions for that. Our unique fingerprint consists precisely of these values.
You can see how easily a website can collect this data and how extensively your actions are identified by websites on this site!
Digital fingerprints: what deserves special attention
Next, I’ll examine popular digital fingerprints used by most major services. I want to note that not all fingerprints will be covered here, and major companies are constantly evolving their security systems, introducing new methods of user identification. Therefore, the ideal solution for working with large companies would be to create and uniquely configure virtual machines. However, this is a resource-intensive task, and for affiliate marketing, you can manage with an Antidetect browser. It needs to be configured properly, and be sure to make the following traces unique:
Font Fingerprint
The font fingerprinting technology, used by all major companies, transmits the list of fonts installed on the user's PC.
For protection, you can disable Flash and JavaScript. You can check the fingerprint trace on Browserscan.
This is a browser API that provides information about the location of elements on a web page, including their size and position. This information is represented as "rectangles" (rects). The reason Client Rects can be used to form a browser's digital fingerprint is that even when opening the same web page on different devices, the information about the location of elements can vary. This occurs due to differences in hardware configuration, operating system, type and version of the browser, screen resolution, font settings, etc.
These differences can be used to create a unique identifier, in other words, a browser fingerprint. For example, on one device's screen, an element may appear larger or smaller than on another device, or be positioned differently on the screen. These differences can be captured using the Client Rects API. More details can be found here.
Canvas
The Canvas API is designed for rendering graphics in web browsers. It can be used for animation, game visualization, data visualization, image editing, real-time video processing, and more. It can also be used for tracking users on the Internet using browser "fingerprints". This technology is based on differences in how images are displayed on the canvas in different web browsers and platforms to create a unique digital fingerprint of the user's browser. More details can be found here.
There are various browser plugins that disable Canvas, for example this one: https://github.com/kkapsner/CanvasBlocker
WebGL
This is a method used for unique identification and tracking of individual users based on specific characteristics of WebGL implementation on their computer. WebGL is a JavaScript API for rendering interactive 2D and 3D graphics in any compatible web browser without using plugins. The fingerprint communicates information about the user's graphics card. More details can be found here.
Audio Fingerprinting
This is a relatively new device tracking technology. The main principle is that due to slight differences in hardware and software configurations, different devices will emit slightly different sounds when playing the same audio file. These differences can be captured and used to create a unique device identifier, in other words, an "audio fingerprint". To protect against fingerprinting, it’s recommended to completely disable JavaScript in the browser, but such drastic measures will make it impossible to use most websites.
WebRTC Fingerprinting
This is the technology underlying audio and video calls in modern browsers. It allows users to connect directly with each other without using intermediary servers. WebRTC can expose your real IP address even if you are using a VPN or TOR. This happens because WebRTC requests the IP addresses of users to establish P2P connections. How to check? You can check if your IP address is leaking via WebRTC on websites like whoer.net or ipleak.net.
Mouse Fingerprint
The technology is based on JavaScript. It tracks user mouse movements, click times, keystrokes, and other parameters. These data create a unique "fingerprint" that can be used for identification purposes.
It’s used in all Anti-fraud systems; do not use automation.
The only reliable way to protect against "Mouse Fingerprinting" is to disable JavaScript in the browser. However, this may cause some websites to function incorrectly.
Сookie and Evercookie
Cookies (cookie files) are small text files that websites save on your device through the browser when you visit them. These files contain information that allows websites to "remember" you and your online activity. Details about how cookies work can be found in the article by the Dolphin Team.
Evercookie is a very persistent type of cookie files. It’s designed to be very difficult to remove: if you try to get rid of it in the usual way, it’ll recreate itself using various hidden places on your computer or browser. Evercookie was developed to demonstrate how difficult it can be to maintain your privacy online when even after removing traces of your presence, they can reappear again.
Evercookie is used in all strong anti-fraud systems, they can be at the PC, Browser level and most often serve for user PC identification. You can read more about the technology here – on Habr. The test is available here: https://whoer.net/evercookie.
When creating a Browser Profile (BP), all these data should be taken into account, because when creating or buying/transferring accounts, it often happens that antidetect browsers do not consider these traces, or you need to enable this uniqueness yourself in the BP settings. If these data are checked by the service you are working with, you may get blocked, even with good warming up, cookies, and proxies. Also, when buying accounts, data is often transmitted through cookies, IPs, and User-Agent, but this data is often insufficient because digital fingerprints differ when transmitted in this way. If you configure your BP incorrectly, you may face blockages.
I recommend using the built-in features for transferring BPs in Antidetect browsers, fortunately, this feature is currently available on all good antidetects.
How to check if your profiles in the Antidetect Browser aren’t linked together?
The easiest way is to open 2 profiles, visit the Browserscan website, and check that all your fingerprints don’t repeat.
You can also visit the website ipleak.net. It’ll show if you have any WEBRTC leaks and if your DNS servers correspond to your GEO.
Practical tips for working with accounts:
- If you're not working alone, try to configure the DNS servers of your GEO or internet provider proxies. If your Antidetect or Proxy doesn't provide this option, use a VPN from the same country as your proxies.
- Always open Browserscan and ipleak.net websites before starting work to ensure your browser is configured correctly.
- Avoid transferring accounts using cookies. Instead, use login credentials or utilize built-in browser functions for account transfer.
- Minimize automation wherever possible, as large companies rapidly develop recognition systems.
- Use high-quality proxies, preferably setting up your own and working on them. Utilize static IP addresses, preferably from the same GEO where the account was registered.
- The GEO-location of your accounts impacts how services treat you, from support availability to potential blockages. Experiment and find GEOs that suit your work needs best.
Use good Antidetect browsers!
I hope the article was useful for you, even if your goal is just to mask your location. However, for working with advertising networks, this may not be enough, and the fingerprint uniqueness features aren’t always enabled by default.

by Editor



comments ....(0)
Leave a comment
You must be in to leave a comment